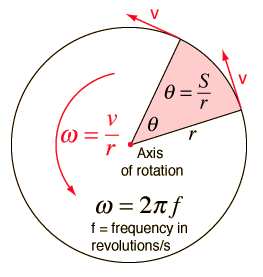
Angular velocity - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Click to enlarge) angular velocity The θ marks an angle of displacement as body . Angular velocity is measured in degrees, radians, or revolutions per unit time. . ->
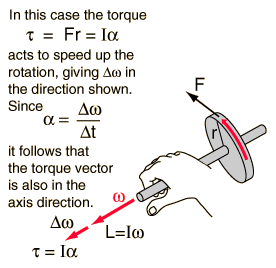
Angular frequency: Definition from Answers.com
angular frequency ( ′angy?l?r ′frēkw?nsē ) ( physics ) For any oscillation, the number of vibrations per unit time, . Do not confuse with angular velocity . ->
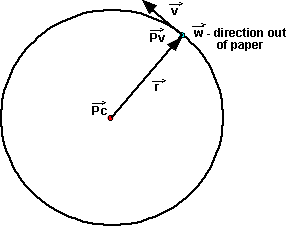
Angular velocity
Average angular velocity of a particle about a point is equal to the ratio of . Instantaneous angular velocity is obtained by taking the limit when time . ->

Physics - Kinematics - Angular Velocity - Martin Baker
. Angular . in two dimensions then we can define angular velocity 'w' in a similar way: . bur to get the angular velocity (w) we need to define the plane that . ->
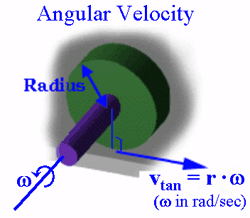
Rotational Quantities
Vector angular velocity . Angular velocity has the units rad/s. Angular velocity is the rate of change of angular displacement and can be . ->
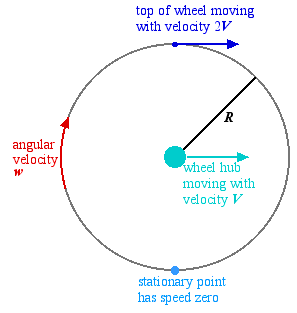
Angular and Linear Velocity
The angular velocity of a particle traveling on a circular path is the ratio of . Therefore, the angular velocity of the Earth's rotation is. . ->

A. Angular Distance θ
B. Angular Velocity ω . angular acceleration are angular velocity divided . And, as in the case of linear motion, the average angular velocity is given by . ->

Talk:Rotational motion/Rotational motion - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
One first introduces the average angular velocity over a time by which the . Angular velocity is measured in radians / second, although for motors in . ->

 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |





















