
Boolean algebra (logic) - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
computer systems operate you will need to understand digital logic and boolean algebra. . controls hardware, the introduction to boolean algebra this chapter . ->
Boolean algebra: Definition from Answers.com
Boolean algebra n. An algebra in which elements have one of two values and the algebraic operations defined on the set are logical OR, a type of ->
Boolean arithmetic : BOOLEAN ALGEBRA
Let us begin our exploration of Boolean algebra by adding numbers together: . Unlike "normal" algebra, though, Boolean variables are always CAPITAL letters, . ->
Boolean algebraic identities : BOOLEAN ALGEBRA
Like ordinary algebra, Boolean algebra has its own unique identities based on . of 2, which has no meaning in Boolean algebra, so we cannot say that A x A = A2. . ->

The Mathematics of Boolean Algebra (Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy)
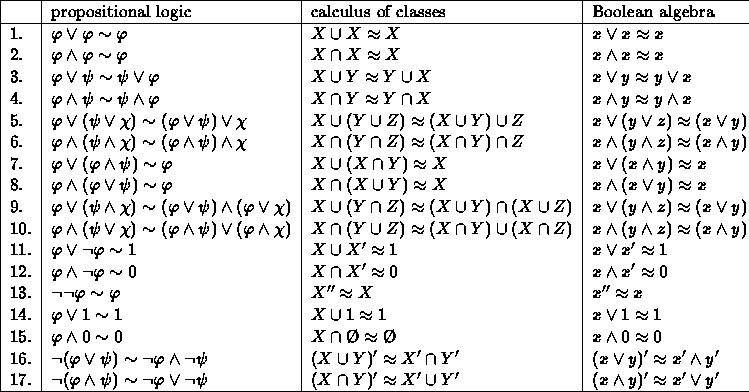
Boolean algebra is the algebra of two-valued logic with only sentential . A Boolean algebra (BA) is a set A together with binary operations + and · and a . ->

Boolean Algebra - Basic Electronic Tutorials
Basic Electronic Tutorials On AC, DC, Semiconductor, and Digital Theory. . Multiplication is valid in Boolean algebra, and thankfully it is the same as in . ->

Electronics/Boolean Algebra - Wikibooks, collection of open-content .
Electronics/Boolean Algebra. From Wikibooks, the open-content textbooks collection . 1.2 Boolean Algebra Laws. 1.2.1 Associativity. 1.2.2 Distributivity . ->

Boolean Algebra
Commutative, Associative laws in normal algebra are the same as. in boolean algebra. . A + BC = (A + B) (A + C) (only valid in Boolean algebra! . ->

 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |





















