Chemical bond - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Chemical Bonding - It introduces the concepts of ionic and covalent bonding. . Anthony Carpi, Ph.D. "Chemical Bonding," Visionlearning Vol. CHE-1 (7), 2003. . ->
Chemical Bonds
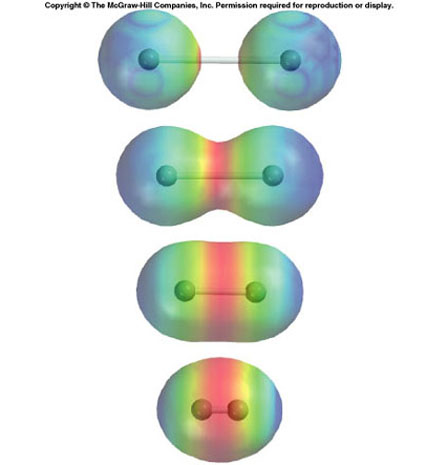
Covalent chemical bonds involve the sharing of a pair of valence electrons by . In chemical bonds, atoms can either transfer or share their valence electrons. . ->
Chemical bonding: Information from Answers.com
Chemical Bonding Concept Almost everything a person sees or touches in daily life-the air we breathe, the food we eat, the clothes we wear, and ->
chemical bond: Definition from Answers.com
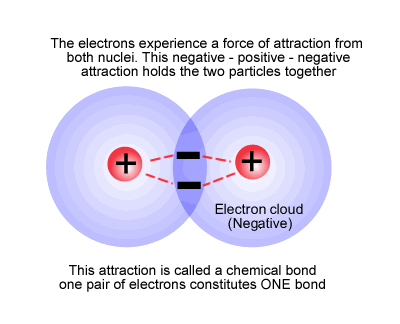
chemical bond n. Any of several forces or mechanisms, especially the ionic bond, covalent bond, and metallic bond, by which atoms or ions are bound in ->
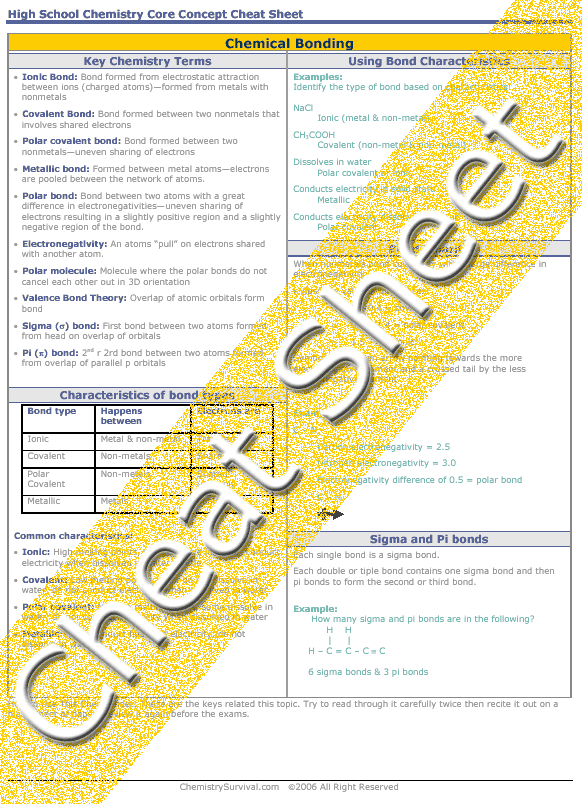
3. Types of Chemical Bonding [Beyond Books - Introduction to Chemistry .
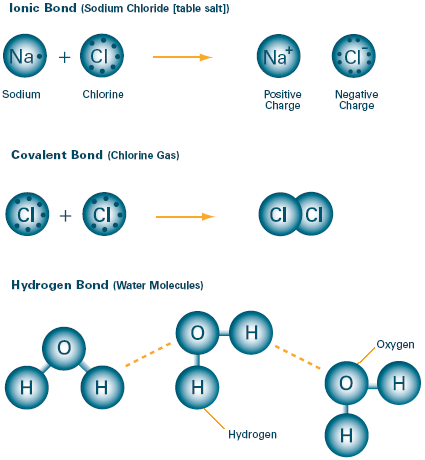
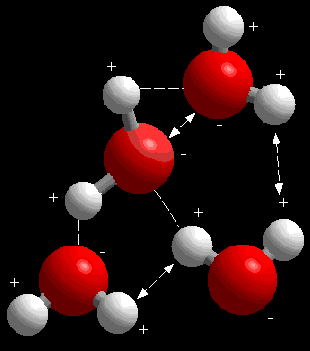
They are held together by CHEMICAL BONDS, strong attractive forces between atoms. . The chemical bonding that takes place in NaCl is different than that in HCl. . ->
Chemical bond Summary and Analysis Summary
Chemical bond summary with 65 pages of encyclopedia entries, essays, summaries, research information, and more. . Chemical Bonds and Physical Properties . ->
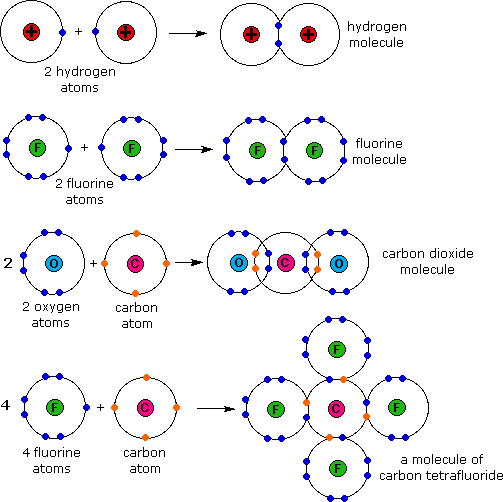
Chemical Bond | World of Biology Summary
Chemical Bond | World of Biology. Chemical Bond summary with 3 pages of encyclopedia entries, research information, and more. ->
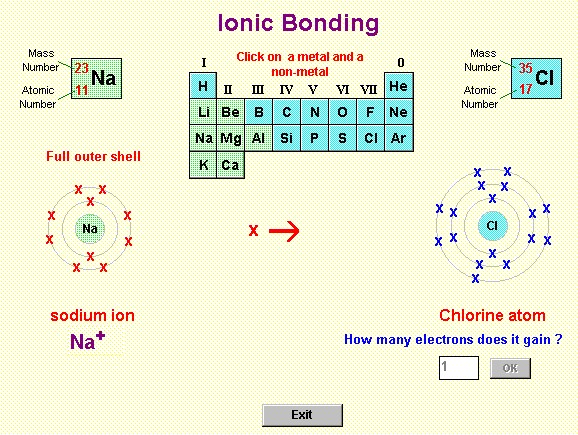
Chemical Bonding
Chemical Bonds. Chemical bonds are interactions of electrons leading to strong forces of . Drawing bonding structures (called Lewis structures) . ->

Chemical bond - New World Encyclopedia
Chemical bonding theory explains one aspect of the relational nature of physical . In the formation of a chemical bond between two atoms (or ions), for example, . ->
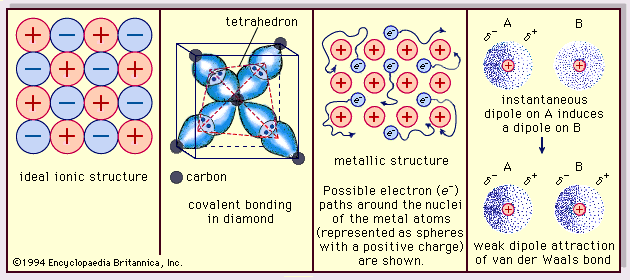
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |





















