
Quantum mechanics - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Quantum theory is the theoretical basis of modern physics that explains the nature and behavior of matter and energy on the atomic and subatomic level. ->

Quantum Theory
. Quantum . for objects that are very small, quantum theory becomes necessary. . sees a neon or sodium light, one is seeing quantum theory in practice. . ->

quantum theory: Definition from Answers.com
quantum theory n. A theory in physics based on the principle that matter and energy have the properties of both particles and waves, created to ->

quantum mechanics: Definition from Answers.com
quantum mechanics n. (used with a sing. or pl. verb) Quantum theory, especially the quantum theory of the structure and behavior of atoms and ->

Encyclopedia.com - Quantum Theory
Get information, facts, and pictures about quantum theory at Encyclopedia.com. . According to the quantum theory, energy is held to be emitted and absorbed in . ->

Quantum Theory
Discovering the fundamental structure of matter. . Quantum theory evolved as a new branch of theoretical physics during the first . ->

Quantum Physics: Quantum Theory / Wave Mechanics
Quantum Physics: Quantum Theory / Wave Mechanics: The Wave Structure of Matter (WSM) and Spherical Standing Wave Interactions explains Discrete Energy States of . ->

Quantum Theory - MSN Encarta
Quantum Theory, in physics, description of the particles that make up matter and . Quantum theory - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia . ->
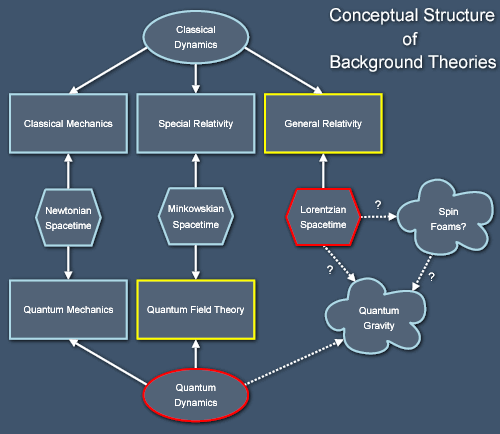
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |





















